- Sha256sum Windows Certutil
- Certutil Hashfile Sha256
- Certutil Command Windows 10
- Certutil Sha256
- Windows 7 Certutil Sha256
- Windows Certutil Md5
- Since SHA1 became insecure and everyone around the web is forcing the change to higher security standards such as SHA256, SHA384 or SHA512 Windows Administrators should also update their internal Microsoft Active Directory Certificate Services to force higher cryptographic provider.
- The following command-line syntax is to be used to calculate the SHA256 checksum of a file using Certutil.exe from a Command Prompt window. Certutil.exe -hashfile filename SHA256. If you want to implement Certutil.exe in your right-click menu, here is a VBScript that exactly does it. Copy the following VBScript code to Notepad.
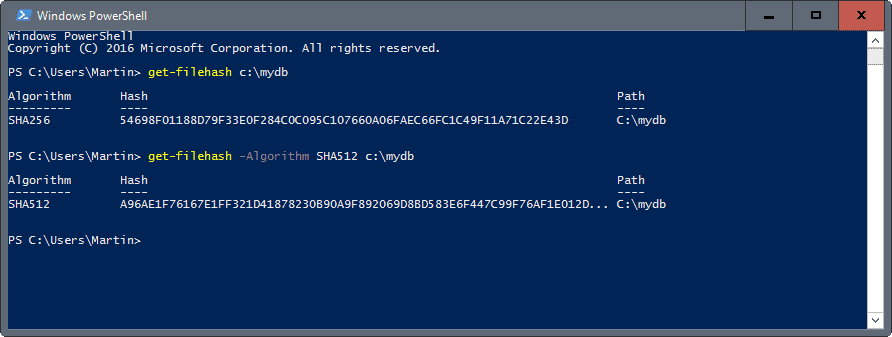
- Press the Windows key. Type PowerShell. Select Windows Powershell. Press Enter key. Paste the command. Get-FileHash C:UsersDonaldDownloadsFile-to-be-checked-by-sha256.exe Format-List. Replace File-to-be-checked-by-sha256.exe by the name of your file to be checked. Replace the path to your path where the file is. Press Enter key.
Mar 31, 2018 This tutorial demonstrates how to verify Hash utilize Certutil in Windows 10. Feel free to comment, like, and subscribe. Command: CertUtil -hashfile 'file name' SHA256 (change the algorithm if it. May 14, 2017 Hello! I need to use this command-line program to get the MD5 hash over a given file in a Microsoft Windows Server 2003 R2, but when I try it this command: certutil -hashfile file.txt md5 I get this error: Expected no more than 1 args, received 2 CertUtil: Too many arguments If I repeat the. Hi, It seems that the certutil on Windows server 2003. Sep 30, 2010 UPDATE (2/8): Based on some recent questions, additional information has been posted about SHA2 and Windows. Introduction We’ve recently received a couple of requests from customers around the functionality of SHA-256 when running on Windows XP and 2003. This has been more important recently, as NIST has recommended the migration off of SHA-1 by end. Mar 09, 2017 Enter certutil, a command-line tool built into Windows. Certutil has many functions, mostly related to viewing and managing certificates, but the –hashfile subcommand can be used on any file to get a hash in MD5, SHA256, or several other formats.
UPDATE (2/8): Based on some recent questions, additional information has been posted about SHA2 and Windows.
We’ve recently received a couple of requests from customers around the functionality of SHA-256 when running on Windows XP and 2003. This has been more important recently, as NIST has recommended the migration off of SHA-1 by end of the year. More details about the NIST recommendation can be found in SP 800-78-2 and SP 800-57. Hopefully this blog post can help clear up the confusion surrounding scenarios that work and the ones that don’t.
Prior to Windows XP Service Pack 3, there was no SHA2 functionality within Windows XP. With the release of Service Pack 3 some limited functionality was added to the crypto module rsaenh.dll. This includes the following SHA2 hashes: SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512. SHA-224 was not included.
Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2 does not ship with support for SHA2. This limitation can become an important concern when processing smart card logons and for mutual TLS authentications to web servers. As unlike other technologies, smart card logon and mutual TLS both use strict revocation checking; so should either the certificate itself or the revocation information (CRL/OCSP) use SHA2, the logon would fail.
KB 938397
Though support SHA2 is not included in Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2, it is available for download. KB 938397 will bring Windows Server 2003 to the same level of functionality as Windows XP with Service Pack 3. KB 938397 is not available via Windows Update; it needs to be requested via the “View and request hotfix downloads” link on the support page. Note, KB 938397 is also offered for Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1.
KB 968730
With the release of Windows Server 2008 it was found that Windows XP Service Pack 3 and Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2 with KB 938397 were unable to request certificates from a Windows Server 2008 (and 2008 R2) certificate authority (CA) who’s certificate was signed with a SHA2 hash. KB 968730 was release to address this issue. Incidentally, KB 968730 completely supersedes KB 938397; so if a Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2 system would need to both enroll from a SHA2 certificate authority and process SHA2 certificates, only KB 968730 would need to be installed. As before, KB 968730 is not available via Windows Update; it needs to be requested via the “View and request hotfix downloads” link on the support page. Note, KB 968730 is not offered for Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1.
Starting with Windows Vista and Server 2008, the Cryptography Next Generation (CNG) Suite B algorithms (including SHA2) are included in the operating system. It is worth noting that even though the algorithms are available, it is up to the individual applications to implement support.
Besides logon, another very popular use for smart cards is S/MIME. But before diving into Outlook and S/MIME, the following warning should be given: Regardless of the functionality Windows and Outlook provide; in order for mail to be delivered between two users, there are any number of spam filters, relays, mailboxes, etc between sender and recipient. Each of these can be made by a wide range of vendors; running on a wide range of platforms. So before deploying SHA2, testing should be done against one’s own email infrastructure, in addition to the email infrastructure of external organizations from whom S/MIME signed mail needs to be exchanged with.
All those warnings aside, the basic functionality for Outlook is a follows. Outlook 2003, 2007, and 2010 running on Windows XP Service Pack 3 can sign and validate certificates when that certificate itself is SHA2 signed. Outlook 2003, 2007, and 2010 running on Windows XP Service Pack 3 cannot validate email messages when the message itself is SHA2 signed (regardless of the certificate used). Outlook 2003, 2007, and 2010 running on Windows XP Service Pack 3 cannot sign a message with SHA2; only SHA-1 and MD5 are available.
In order to validate SHA2 messages, Windows Vista with Outlook 2003 (or newer) is needed. In order to both sign and validate SHA2 messages, Windows Vista or 7 with Outlook 2007 or 2010 is needed.
For organizations looking to deploy SHA2 or organizations that interact with 3rd parties that will soon begin using SHA2, the following is recommended.
- If Windows XP is used in the environment, Service Pack 3 should be deployed. In addition to SHA2 functionality, Service Pack 3 is currently the only Windows XP service pack that is supported.
- If Windows XP systems would need to enroll in certificates from a SHA2 certificate authority, KB 968730 should be deployed.
- If Windows Server 2003 is used in the environment, Service Pack (1 or 2) and KB 938397 should be deployed.
- If Windows Server 2003 would need to enroll in certificates from a SHA2 certificate authority, Service Pack 2 and KB 968730 should be deployed. If planning on deploying KB 968730, installing KB 938397 is not necessary.
- If S/MIME using SHA2 signing for the message body is needed, workstations should be upgraded to at least Windows Vista running Office 2003.
XP SP3 | XP SP3 with KB968730 | 2003 R2 SP2 | 2003 R2 SP2 with KB968730 | Windows Vista, 7, 2008, 2008 R2 | |
Basic Functionality | |||||
Browsing a website using SHA2 certificate | Works | Works | Unable to validate certificate | Works | Works |
Open a certificate and viewing properties | Works | Works | Unable to validate certificate | Works | Works |
Interactive logon and mutual TLS (client system) | |||||
Client with SHA2 certificate; server with SHA1 certificate | Works | Works | Works | Works | Works |
Client with SHA2 certificate; server with SHA2 certificate | Works | Works | Unable to login | Works | Works |
Interactive logon and mutual TLS (domain controller / IIS server) | |||||
Client with SHA2 certificate; server with SHA1 certificate | N/A | N/A | Unable to login | Works | Works |
Certificate Enrollment | |||||
V3 certificate template enrollment from any type of root | Unable to select template | Unable to select template | Unable to select template | Unable to select template | Works |
V2 certificate template enrollment from SHA2 root | Request fails | Works | Request fails | Works | Works |
S/MIME (Outlook 2003) | |||||
Validate and sign to a SHA2 certificate | Works | Works | N/A | N/A | Works |
Validate message body signed with SHA2 | Unable to validate certificate | Unable to validate certificate | N/A | N/A | Works |
Sign message body with SHA2 | Not an available option | Not an available option | N/A | N/A | Not an available option |
S/MIME (Outlook 2007 and 2010) | |||||
Validate and sign to a SHA2 certificate using SHA-1 for the message signature | Works | Works | N/A | N/A | Works |
Validate message body signed with SHA2 | Unable to validate certificate | Unable to validate certificate | N/A | N/A | Works |
Sign message body with SHA2 | Not an available option | Not an available option | N/A | N/A | Works |
-Adam Stasiniewicz
UPDATE (2/8): Based on some recent questions, additional information has been posted about SHA2 and Windows.
-->Certutil.exe is a command-line program that is installed as part of Certificate Services. You can use Certutil.exe to dump and display certification authority (CA) configuration information, configure Certificate Services, backup and restore CA components, and verify certificates, key pairs, and certificate chains.
When certutil is run on a certification authority without additional parameters, it displays the current certification authority configuration. When cerutil is run on a non-certification authority, the command defaults to running the certutil -dump verb.
Warning
Earlier versions of certutil may not provide all of the options that are described in this document. You can see all the options that a specific version of certutil provides by running the commands shown in the Syntax notations section.
Menu
The major sections in this document are:
Verbs
The following table describes the verbs that can be used with the certutil command.
| Verbs | Description |
|---|---|
| -dump | Dump configuration information or files |
| -asn | Parse ASN.1 file |
| -decodehex | Decode hexadecimal-encoded file |
| -decode | Decode a Base64-encoded file |
| -encode | Encode a file to Base64 |
| -deny | Deny a pending certificate request |
| -resubmit | Resubmit a pending certificate request |
| -setattributes | Set attributes for a pending certificate request |
| -setextension | Set an extension for a pending certificate request |
| -revoke | Revoke a certificate |
| -isvalid | Display the disposition of the current certificate |
| -getconfig | Get the default configuration string |
| -ping | Attempt to contact the Active Directory Certificate Services Request interface |
| -pingadmin | Attempt to contact the Active Directory Certificate Services Admin interface |
| -CAInfo | Display information about the certification authority |
| -ca.cert | Retrieve the certificate for the certification authority |
| -ca.chain | Retrieve the certificate chain for the certification authority |
| -GetCRL | Get a certificate revocation list (CRL) |
| -CRL | Publish new certificate revocation lists (CRLs) [or only delta CRLs] |
| -shutdown | Shutdown Active Directory Certificate Services |
| -installCert | Install a certification authority certificate |
| -renewCert | Renew a certification authority certificate |
| -schema | Dump the schema for the certificate |
| -view | Dump the certificate view |
| -db | Dump the raw database |
| -deleterow | Delete a row from the server database |
| -backup | Backup Active Directory Certificate Services |
| -backupDB | Backup the Active Directory Certificate Services database |
| -backupKey | Backup the Active Directory Certificate Services certificate and private key |
| -restore | Restore Active Directory Certificate Services |
| -restoreDB | Restore the Active Directory Certificate Services database |
| -restoreKey | Restore the Active Directory Certificate Services certificate and private key |
| -importPFX | Import certificate and private key |
| -dynamicfilelist | Display a dynamic file list |
| -databaselocations | Display database locations |
| -hashfile | Generate and display a cryptographic hash over a file |
| -store | Dump the certificate store |
| -addstore | Add a certificate to the store |
| -delstore | Delete a certificate from the store |
| -verifystore | Verify a certificate in the store |
| -repairstore | Repair a key association or update certificate properties or the key security descriptor |
| -viewstore | Dump the certificates store |
| -viewdelstore | Delete a certificate from the store |
| -dsPublish | Publish a certificate or certificate revocation list (CRL) to Active Directory |
| -ADTemplate | Display AD templates |
| -Template | Display certificate templates |
| -TemplateCAs | Display the certification authorities (CAs) for a certificate template |
| -CATemplates | Display templates for CA |
| -SetCASites | Manage Site Names for CAs |
| -enrollmentServerURL | Display, add or delete enrollment server URLs associated with a CA |
| -ADCA | Display AD CAs |
| -CA | Display Enrollment Policy CAs |
| -Policy | Display Enrollment Policy |
| -PolicyCache | Display or delete Enrollment Policy Cache entries |
| -CredStore | Display, add or delete Credential Store entries |
| -InstallDefaultTemplates | Install default certificate templates |
| -URLCache | Display or delete URL cache entries |
| -pulse | Pulse auto enrollment events |
| -MachineInfo | Display information about the Active Directory machine object |
| -DCInfo | Display information about the domain controller |
| -EntInfo | Display information about an enterprise CA |
| -TCAInfo | Display information about the CA |
| -SCInfo | Display information about the smart card |
| -SCRoots | Manage smart card root certificates |
| -verifykeys | Verify a public or private key set |
| -verify | Verify a certificate, certificate revocation list (CRL), or certificate chain |
| -verifyCTL | Verify AuthRoot or Disallowed Certificates CTL |
| -sign | Re-sign a certificate revocation list (CRL) or certificate |
| -vroot | Create or delete web virtual roots and file shares |
| -vocsproot | Create or delete web virtual roots for an OCSP web proxy |
| -addEnrollmentServer | Add an Enrollment Server application |
| -deleteEnrollmentServer | Delete an Enrollment Server application |
| -addPolicyServer | Add a Policy Server application |
| -deletePolicyServer | Delete a Policy Server application |
| -oid | Display the object identifier or set a display name |
| -error | Display the message text associated with an error code |
| -getreg | Display a registry value |
| -setreg | Set a registry value |
| -delreg | Delete a registry value |
| -ImportKMS | Import user keys and certificates into the server database for key archival |
| -ImportCert | Import a certificate file into the database |
| -GetKey | Retrieve an archived private key recovery blob |
| -RecoverKey | Recover an archived private key |
| -MergePFX | Merge PFX files |
| -ConvertEPF | Convert a PFX file into an EPF file |
| -? | Displays the list of verbs |
| -<verb> -? | Displays help for the verb specified. |
| -? -v | Displays a full list of verbs and |
Return to Menu
Syntax notations
- For basic command line syntax, run
certutil -? - For the syntax on using certutil with a specific verb, run certutil<verb>-?
- To send all of the certutil syntax into a text file, run the following commands:
certutil -v -? > certutilhelp.txtnotepad certutilhelp.txt
The following table describes the notation used to indicate command-line syntax.
| Notation | Description |
|---|---|
| Text without brackets or braces | Items you must type as shown |
| <Text inside angle brackets> | Placeholder for which you must supply a value |
| [Text inside square brackets] | Optional items |
| {Text inside braces} | Set of required items; choose one |
| Vertical bar ( | ) |
| Ellipsis (…) | Items that can be repeated |
Return to Menu
-dump
CertUtil [Options] [-dump]
CertUtil [Options] [-dump] File
Dump configuration information or files
[-f] [-silent] [-split] [-p Password] [-t Timeout]
Return to Menu
-asn
CertUtil [Options] -asn File [type]
Parse ASN.1 file
type: numeric CRYPT_STRING_* decoding type
Return to Menu
-decodehex
CertUtil [Options] -decodehex InFile OutFile [type]
type: numeric CRYPT_STRING_* encoding type
[-f]
Return to Menu
-decode
CertUtil [Options] -decode InFile OutFile
Decode Base64-encoded file
[-f]
Return to Menu
-encode
CertUtil [Options] -encode InFile OutFile
Encode file to Base64
[-f] [-UnicodeText]
Return to Menu
-deny
CertUtil [Options] -deny RequestId
Deny pending request
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-resubmit
CertUtil [Options] -resubmit RequestId
Resubmit pending request
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-setattributes
CertUtil [Options] -setattributes RequestId AttributeString
Set attributes for pending request
RequestId -- numeric Request Id of pending request
AttributeString -- Request Attribute name and value pairs
- Names and values are colon separated.
- Multiple name, value pairs are newline separated.
- Example: 'CertificateTemplate:UsernEMail:User@Domain.com'
- Each 'n' sequence is converted to a newline separator.
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-setextension
CertUtil [Options] -setextension RequestId ExtensionName Flags {Long | Date | String | @InFile}
Set extension for pending request
RequestId -- numeric Request Id of a pending request
ExtensionName -- ObjectId string of the extension
Flags -- 0 is recommended. 1 makes the extension critical, 2 disables it, 3 does both.
If the last parameter is numeric, it is taken as a Long.
If it can be parsed as a date, it is taken as a Date.
If it starts with '@', the rest of the token is the filename containing binary data or an ascii-text hex dump.
Anything else is taken as a String.
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-revoke
CertUtil [Options] -revoke SerialNumber [Reason]
Revoke Certificate
SerialNumber: Comma separated list of certificate serial numbers to revoke
Reason: numeric or symbolic revocation reason
- 0: CRL_REASON_UNSPECIFIED: Unspecified (default)
- 1: CRL_REASON_KEY_COMPROMISE: Key Compromise
- 2: CRL_REASON_CA_COMPROMISE: CA Compromise
- 3: CRL_REASON_AFFILIATION_CHANGED: Affiliation Changed
- 4: CRL_REASON_SUPERSEDED: Superseded
- 5: CRL_REASON_CESSATION_OF_OPERATION: Cessation of Operation
- 6: CRL_REASON_CERTIFICATE_HOLD: Certificate Hold
- 8: CRL_REASON_REMOVE_FROM_CRL: Remove From CRL
- -1: Unrevoke: Unrevoke
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-isvalid
CertUtil [Options] -isvalid SerialNumber | CertHash
Display current certificate disposition
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-getconfig
CertUtil [Options] -getconfig
Get default configuration string
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-ping
CertUtil [Options] -ping [MaxSecondsToWait | CAMachineList]
Ping Active Directory Certificate Services Request interface
CAMachineList -- Comma-separated CA machine name list
- For a single machine, use a terminating comma
- Displays the site cost for each CA machine
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-CAInfo
CertUtil [Options] -CAInfo [InfoName [Index | ErrorCode]]
Display CA Information
InfoName -- indicates the CA property to display (see below). Use '*' for all properties.
Index -- optional zero-based property index
ErrorCode -- numeric error code
[-f] [-split] [-config MachineCAName]
InfoName argument syntax:
- file: File version
- product: Product version
- exitcount: Exit module count
- exit [Index]: Exit module description
- policy: Policy module description
- name: CA name
- sanitizedname: Sanitized CA name
- dsname: Sanitized CA short name (DS name)
- sharedfolder: Shared folder
- error1 ErrorCode: Error message text
- error2 ErrorCode: Error message text and error code
- type: CA type
- info: CA info
- parent: Parent CA
- certcount: CA cert count
- xchgcount: CA exchange cert count
- kracount: KRA cert count
- kraused: KRA cert used count
- propidmax: Maximum CA PropId
- certstate [Index]: CA cert
- certversion [Index]: CA cert version
- certstatuscode [Index]: CA cert verify status
- crlstate [Index]: CRL
- krastate [Index]: KRA cert
- crossstate+ [Index]: Forward cross cert
- crossstate- [Index]: Backward cross cert
- cert [Index]: CA cert
- certchain [Index]: CA cert chain
- certcrlchain [Index]: CA cert chain with CRLs
- xchg [Index]: CA exchange cert
- xchgchain [Index]: CA exchange cert chain
- xchgcrlchain [Index]: CA exchange cert chain with CRLs
- kra [Index]: KRA cert
- cross+ [Index]: Forward cross cert
- cross- [Index]: Backward cross cert
- CRL [Index]: Base CRL
- deltacrl [Index]: Delta CRL
- crlstatus [Index]: CRL Publish Status
- deltacrlstatus [Index]: Delta CRL Publish Status
- dns: DNS Name
- role: Role Separation
- ads: Advanced Server
- templates: Templates
- csp [Index]: OCSP URLs
- aia [Index]: AIA URLs
- cdp [Index]: CDP URLs
- localename: CA locale name
- subjecttemplateoids: Subject Template OIDs
Return to Menu
-ca.cert
CertUtil [Options] -ca.cert OutCACertFile [Index]
Retrieve the CA's certificate
OutCACertFile: output file
Index: CA certificate renewal index (defaults to most recent)
[-f] [-split] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-ca.chain
CertUtil [Options] -ca.chain OutCACertChainFile [Index]
Retrieve the CA's certificate chain
OutCACertChainFile: output file
Index: CA certificate renewal index (defaults to most recent)
[-f] [-split] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-GetCRL
CertUtil [Options] -GetCRL OutFile [Index] [delta]
Get CRL
Index: CRL index or key index (defaults to CRL for newest key)
delta: delta CRL (default is base CRL)
[-f] [-split] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-CRL
CertUtil [Options] -CRL [dd:hh | republish] [delta]
Publish new CRLs [or delta CRLs only]
dd:hh -- new CRL validity period in days and hours
republish -- republish most recent CRLs
delta -- delta CRLs only (default is base and delta CRLs)
[-split] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-shutdown
CertUtil [Options] -shutdown
Shutdown Active Directory Certificate Services
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-installCert
CertUtil [Options] -installCert [CACertFile]
Install Certification Authority certificate
[-f] [-silent] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-renewCert
CertUtil [Options] -renewCert [ReuseKeys] [MachineParentCAName]
Renew Certification Authority certificate
Use -f to ignore an outstanding renewal request, and generate a new request.
[-f] [-silent] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-schema
CertUtil [Options] -schema [Ext | Attrib | CRL]
Dump Certificate Schema
Defaults to Request and Certificate table
Ext: Extension table
Attrib: Attribute table
CRL: CRL table
[-split] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-view
CertUtil [Options] -view [Queue | Log | LogFail | Revoked | Ext | Attrib | CRL] [csv]
Dump Certificate View
Queue: Request queue
Log: Issued or revoked certificates, plus failed requests
LogFail: Failed requests
Revoked: Revoked certificates
Ext: Extension table
Attrib: Attribute table
CRL: CRL table
csv: Output as Comma Separated Values
To display the StatusCode column for all entries: -out StatusCode
To display all columns for the last entry: -restrict 'RequestId$'
To display RequestId and Disposition for three requests: -restrict 'RequestId>=37,RequestId<40' -out 'RequestId,Disposition'
To display Row Ids and CRL Numbers for all Base CRLs: -restrict 'CRLMinBase=0' -out 'CRLRowId,CRLNumber' CRL
To display Base CRL Number 3: -v -restrict 'CRLMinBase=0,CRLNumber=3' -out 'CRLRawCRL' CRL
To display the entire CRL table: CRL
Use 'Date[+|-dd:hh]' for date restrictions
Use 'now+dd:hh' for a date relative to the current time
[-silent] [-split] [-config MachineCAName] [-restrict RestrictionList] [-out ColumnList]
Return to Menu
-db
CertUtil [Options] -db
Dump Raw Database
[-config MachineCAName] [-restrict RestrictionList] [-out ColumnList]
Return to Menu
-deleterow
CertUtil [Options] -deleterow RowId | Date [Request | Cert | Ext | Attrib | CRL]
Delete server database row
Request: Failed and pending requests (submission date)
Cert: Expired and revoked certificates (expiration date)
Ext: Extension table
Attrib: Attribute table
CRL: CRL table (expiration date)
To delete failed and pending requests submitted by January 22, 2001: 1/22/2001 Request
To delete all certificates that expired by January 22, 2001: 1/22/2001 Cert
To delete the certificate row, attributes and extensions for RequestId 37: 37
To delete CRLs that expired by January 22, 2001: 1/22/2001 CRL
[-f] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-backup
CertUtil [Options] -backup BackupDirectory [Incremental] [KeepLog]
Backup Active Directory Certificate Services
BackupDirectory: directory to store backed up data
Incremental: perform incremental backup only (default is full backup)
KeepLog: preserve database log files (default is to truncate log files)
[-f] [-config MachineCAName] [-p Password]
Return to Menu
-backupDB
CertUtil [Options] -backupDB BackupDirectory [Incremental] [KeepLog]
Backup Active Directory Certificate Services database
BackupDirectory: directory to store backed up database files
Incremental: perform incremental backup only (default is full backup)
KeepLog: preserve database log files (default is to truncate log files)
[-f] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-backupKey
CertUtil [Options] -backupKey BackupDirectory
Backup Active Directory Certificate Services certificate and private key
BackupDirectory: directory to store backed up PFX file
[-f] [-config MachineCAName] [-p Password] [-t Timeout]
Return to Menu
-restore
CertUtil [Options] -restore BackupDirectory
Restore Active Directory Certificate Services
BackupDirectory: directory containing data to be restored
[-f] [-config MachineCAName] [-p Password]
Return to Menu
-restoreDB
CertUtil [Options] -restoreDB BackupDirectory
Restore Active Directory Certificate Services database
BackupDirectory: directory containing database files to be restored
[-f] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-restoreKey
CertUtil [Options] -restoreKey BackupDirectory | PFXFile
Restore Active Directory Certificate Services certificate and private key
BackupDirectory: directory containing PFX file to be restored
PFXFile: PFX file to be restored
[-f] [-config MachineCAName] [-p Password]
Return to Menu
-importPFX
CertUtil [Options] -importPFX [CertificateStoreName] PFXFile [Modifiers]
Import certificate and private key
CertificateStoreName: Certificate store name. Transfer whatsapp from android to iphone free app. See -store.
PFXFile: PFX file to be imported
Modifiers: Comma separated list of one or more of the following:
- AT_SIGNATURE: Change the KeySpec to Signature
- AT_KEYEXCHANGE: Change the KeySpec to Key Exchange
- NoExport: Make the private key non-exportable
- NoCert: Do not import the certificate
- NoChain: Do not import the certificate chain
- NoRoot: Do not import the root certificate
- Protect: Protect keys with password
- NoProtect: Do not password protect keys
Defaults to personal machine store.
[-f] [-user] [-p Password] [-csp Provider]
But some cannot be downloaded because they include features that cannot be printed, for example a clear plastic window to attach a photo. Before you startYou can order the following forms to be posted to a UK address.You can download some of them. https://luckytp.netlify.app/dvla-d1-form-download.html.
Return to Menu
-dynamicfilelist
CertUtil [Options] -dynamicfilelist
Display dynamic file List
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-databaselocations
CertUtil [Options] -databaselocations
Display database locations
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-hashfile
CertUtil [Options] -hashfile InFile [HashAlgorithm]
Generate and display cryptographic hash over a file
Return to Menu
-store
CertUtil [Options] -store [CertificateStoreName [CertId [OutputFile]]]
Dump certificate store
CertificateStoreName: Certificate store name. Examples:
- 'My', 'CA' (default), 'Root',
- 'ldap:///CN=Certification Authorities,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=cpandl,DC=com?cACertificate?one?objectClass=certificationAuthority' (View Root Certificates)
- 'ldap:///CN=CAName,CN=Certification Authorities,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=cpandl,DC=com?cACertificate?base?objectClass=certificationAuthority' (Modify Root Certificates)
- 'ldap:///CN=CAName,CN=MachineName,CN=CDP,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=cpandl,DC=com?certificateRevocationList?base?objectClass=cRLDistributionPoint' (View CRLs)
- 'ldap:///CN=NTAuthCertificates,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=cpandl,DC=com?cACertificate?base?objectClass=certificationAuthority' (Enterprise CA Certificates)
- ldap: (AD computer object certificates)
- -user ldap: (AD user object certificates)
CertId: Certificate or CRL match token. This can be a serial number, an SHA-1 certificate, CRL, CTL or public key hash, a numeric cert index (0, 1, and so on), a numeric CRL index (.0, .1, and so on), a numeric CTL index (.0, .1, and so on), a public key, signature or extension ObjectId, a certificate subject Common Name, an e-mail address, UPN or DNS name, a key container name or CSP name, a template name or ObjectId, an EKU or Application Policies ObjectId, or a CRL issuer Common Name. Many of these may result in multiple matches.
OutputFile: file to save matching cert
Use -user to access a user store instead of a machine store.
Use -enterprise to access a machine enterprise store.
Use -service to access a machine service store.
Use -grouppolicy to access a machine group policy store.
Examples:
- -enterprise NTAuth
- -enterprise Root 37
- -user My 26e0aaaf000000000004
- CA .11
[-f] [-enterprise] [-user] [-GroupPolicy] [-silent] [-split] [-dc DCName]
Return to Menu
-addstore
CertUtil [Options] -addstore CertificateStoreName InFile
Add certificate to store
CertificateStoreName: Certificate store name. See -store.
InFile: Certificate or CRL file to add to store.
[-f] [-enterprise] [-user] [-GroupPolicy] [-dc DCName]
Return to Menu
-delstore
CertUtil [Options] -delstore CertificateStoreName CertId
Delete certificate from store
CertificateStoreName: Certificate store name. See -store.
CertId: Certificate or CRL match token. See -store.
[-enterprise] [-user] [-GroupPolicy] [-dc DCName]
Return to Menu
-verifystore
CertUtil [Options] -verifystore CertificateStoreName [CertId]
Verify certificate in store
CertificateStoreName: Certificate store name. See -store.
CertId: Certificate or CRL match token. See -store.
[-enterprise] [-user] [-GroupPolicy] [-silent] [-split] [-dc DCName] [-t Timeout]
Return to Menu
-repairstore
CertUtil [Options] -repairstore CertificateStoreName CertIdList [PropertyInfFile | SDDLSecurityDescriptor]
Repair key association or update certificate properties or key security descriptor
CertificateStoreName: Certificate store name. See -store.
CertIdList: comma separated list of Certificate or CRL match tokens. See -store CertId description.
PropertyInfFile -- INF file containing external properties:
[-f] [-enterprise] [-user] [-GroupPolicy] [-silent] [-split] [-csp Provider]
Return to Menu
-viewstore
CertUtil [Options] -viewstore [CertificateStoreName [CertId [OutputFile]]]
Dump certificate store
CertificateStoreName: Certificate store name. Examples:
- 'My', 'CA' (default), 'Root',
- 'ldap:///CN=Certification Authorities,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=cpandl,DC=com?cACertificate?one?objectClass=certificationAuthority' (View Root Certificates)
- 'ldap:///CN=CAName,CN=Certification Authorities,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=cpandl,DC=com?cACertificate?base?objectClass=certificationAuthority' (Modify Root Certificates)
- 'ldap:///CN=CAName,CN=MachineName,CN=CDP,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=cpandl,DC=com?certificateRevocationList?base?objectClass=cRLDistributionPoint' (View CRLs)
- 'ldap:///CN=NTAuthCertificates,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=cpandl,DC=com?cACertificate?base?objectClass=certificationAuthority' (Enterprise CA Certificates)
- ldap: (AD machine object certificates)
- -user ldap: (AD user object certificates)
CertId: Certificate or CRL match token. This can be a serial number, an SHA-1 certificate, CRL, CTL or public key hash, a numeric cert index (0, 1, and so on), a numeric CRL index (.0, .1, and so on), a numeric CTL index (.0, .1, and so on), a public key, signature or extension ObjectId, a certificate subject Common Name, an e-mail address, UPN or DNS name, a key container name or CSP name, a template name or ObjectId, an EKU or Application Policies ObjectId, or a CRL issuer Common Name. Many of these may result in multiple matches.
OutputFile: file to save matching cert
Use -user to access a user store instead of a machine store.
Use -enterprise to access a machine enterprise store.
Use -service to access a machine service store.
Use -grouppolicy to access a machine group policy store.
Examples:
- -enterprise NTAuth
- -enterprise Root 37
- -user My 26e0aaaf000000000004
- CA .11
[-f] [-enterprise] [-user] [-GroupPolicy] [-dc DCName]
Return to Menu
-viewdelstore
CertUtil [Options] -viewdelstore [CertificateStoreName [CertId [OutputFile]]]
Delete certificate from store
CertificateStoreName: Certificate store name. Examples:
- 'My', 'CA' (default), 'Root',
- 'ldap:///CN=Certification Authorities,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=cpandl,DC=com?cACertificate?one?objectClass=certificationAuthority' (View Root Certificates)
- 'ldap:///CN=CAName,CN=Certification Authorities,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=cpandl,DC=com?cACertificate?base?objectClass=certificationAuthority' (Modify Root Certificates)
- 'ldap:///CN=CAName,CN=MachineName,CN=CDP,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=cpandl,DC=com?certificateRevocationList?base?objectClass=cRLDistributionPoint' (View CRLs)
- 'ldap:///CN=NTAuthCertificates,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=Configuration,DC=cpandl,DC=com?cACertificate?base?objectClass=certificationAuthority' (Enterprise CA Certificates)
- ldap: (AD machine object certificates)
- -user ldap: (AD user object certificates)
CertId: Certificate or CRL match token. This can be a serial number, an SHA-1 certificate, CRL, CTL or public key hash, a numeric cert index (0, 1, and so on), a numeric CRL index (.0, .1, and so on), a numeric CTL index (.0, .1, and so on), a public key, signature or extension ObjectId, a certificate subject Common Name, an e-mail address, UPN or DNS name, a key container name or CSP name, a template name or ObjectId, an EKU or Application Policies ObjectId, or a CRL issuer Common Name. Many of these may result in multiple matches.
OutputFile: file to save matching cert
Use -user to access a user store instead of a machine store.
Use -enterprise to access a machine enterprise store.
Use -service to access a machine service store.
Use -grouppolicy to access a machine group policy store.
Examples:
- -enterprise NTAuth
- -enterprise Root 37
- -user My 26e0aaaf000000000004
- CA .11
[-f] [-enterprise] [-user] [-GroupPolicy] [-dc DCName]
Return to Menu
-dsPublish
CertUtil [Options] -dsPublish CertFile [NTAuthCA | RootCA | SubCA | CrossCA | KRA | User | Machine]
CertUtil [Options] -dsPublish CRLFile [DSCDPContainer [DSCDPCN]]
Publish certificate or CRL to Active Directory
CertFile: certificate file to publish
NTAuthCA: Publish cert to DS Enterprise store
RootCA: Publish cert to DS Trusted Root store
SubCA: Publish CA cert to DS CA object
CrossCA: Publish cross cert to DS CA object
KRA: Publish cert to DS Key Recovery Agent object
User: Publish cert to User DS object
Machine: Publish cert to Machine DS object
CRLFile: CRL file to publish
DSCDPContainer: DS CDP container CN, usually the CA machine name
DSCDPCN: DS CDP object CN, usually based on the sanitized CA short name and key index
Use -f to create DS object.
[-f] [-user] [-dc DCName]
Return to Menu
-ADTemplate
CertUtil [Options] -ADTemplate [Template]
Display AD templates
[-f] [-user] [-ut] [-mt] [-dc DCName]
-Template
CertUtil [Options] -Template [Template]
Display Enrollment Policy templates
[-f] [-user] [-silent] [-PolicyServer URLOrId] [-Anonymous] [-Kerberos] [-ClientCertificate ClientCertId] [-UserName UserName] [-p Password]
Return to Menu
-TemplateCAs
CertUtil [Options] -TemplateCAs Template
Display CAs for template
[-f] [-user] [-dc DCName]
Return to Menu
-CATemplates
CertUtil [Options] -CATemplates [Template]
Display templates for CA
[-f] [-user] [-ut] [-mt] [-config MachineCAName] [-dc DCName]
Return to Menu
-SetCASites
Sha256sum Windows Certutil
CertUtil [Options] -SetCASites [set] [SiteName]
CertUtil [Options] -SetCASites verify [SiteName]
CertUtil [Options] -SetCASites delete
Set, Verify or Delete CA site names
- Use the -config option to target a single CA (Default is all CAs)
- SiteName is allowed only when targeting a single CA
- Use -f to override validation errors for the specified SiteName
- Use -f to delete all CA site names
[-f] [-config MachineCAName] [-dc DCName]
Note
For more information on configuring CAs for Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) site awareness, see AD DS Site Awareness for AD CS and PKI clients.
Return to Menu
-enrollmentServerURL
CertUtil [Options] -enrollmentServerURL [URL AuthenticationType [Priority] [Modifiers]]
CertUtil [Options] -enrollmentServerURL URL delete
Display, add or delete enrollment server URLs associated with a CA
AuthenticationType: Specify one of the following client authentication methods while adding a URL
- Kerberos: Use Kerberos SSL credentials
- UserName: Use named account for SSL credentials
- ClientCertificate: Use X.509 Certificate SSL credentials
- Anonymous: Use anonymous SSL credentials
delete: deletes the specified URL associated with the CA
Priority: defaults to '1' if not specified when adding a URL
Modifiers -- Comma separated list of one or more of the following:
- AllowRenewalsOnly: Only renewal requests can be submitted to this CA via this URL
- AllowKeyBasedRenewal: Allows use of a certificate that has no associated account in the AD. This applies only with ClientCertificate and AllowRenewalsOnly Mode
[-config MachineCAName] [-dc DCName]
Return to Menu
-ADCA
CertUtil [Options] -ADCA [CAName]
Display AD CAs
[-f] [-split] [-dc DCName]
Return to Menu
-CA
CertUtil [Options] -CA [CAName | TemplateName]
Display Enrollment Policy CAs
[-f] [-user] [-silent] [-split] [-PolicyServer URLOrId] [-Anonymous] [-Kerberos] [-ClientCertificate ClientCertId] [-UserName UserName] [-p Password]
Return to Menu
-Policy
Display Enrollment Policy
[-f] [-user] [-silent] [-split] [-PolicyServer URLOrId] [-Anonymous] [-Kerberos] [-ClientCertificate ClientCertId] [-UserName UserName] [-p Password]
Return to Menu
-PolicyCache
CertUtil [Options] -PolicyCache [delete]
Display or delete Enrollment Policy Cache entries
delete: delete Policy Server cache entries
-f: use -f to delete all cache entries
[-f] [-user] [-PolicyServer URLOrId]
Return to Menu
-CredStore
CertUtil [Options] -CredStore windows-certutil-sha256.html
CertUtil [Options] -CredStore URL add
CertUtil [Options] -CredStore URL delete
Display, add or delete Credential Store entries
URL: target URL. Use * to match all entries. Use https://machine* to match a URL prefix.
add: add a Credential Store entry. SSL credentials must also be specified.
delete: delete Credential Store entries
-f: use -f to overwrite an entry or to delete multiple entries.
[-f] [-user] [-silent] [-Anonymous] [-Kerberos] [-ClientCertificate ClientCertId] [-UserName UserName] [-p Password]
Return to Menu
-InstallDefaultTemplates
CertUtil [Options] -InstallDefaultTemplates
Install default certificate templates
[-dc DCName]
Return to Menu
-URLCache
CertUtil [Options] -URLCache [URL | CRL | * [delete]]
Display or delete URL cache entries
URL: cached URL
CRL: operate on all cached CRL URLs only
*: operate on all cached URLs
delete: delete relevant URLs from the current user's local cache
Use -f to force fetching a specific URL and updating the cache.
[-f] [-split]
Return to Menu
-pulse
CertUtil [Options] -pulse
Pulse autoenrollment events
[-user]
Return to Menu
-MachineInfo
CertUtil [Options] -MachineInfo DomainNameMachineName$
Display Active Directory computer object information
Return to Menu
-DCInfo
CertUtil [Options] -DCInfo [Domain] [Verify | DeleteBad | DeleteAll]
Display domain controller information
Default is to display DC certs without verification
[-f] [-user] [-urlfetch] [-dc DCName] [-t Timeout]
Tip
The ability to specify an Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain [Domain] and to specify a domain controller (-dc) was added in Windows Server 2012. To successfully run the command, you must use an account that is a member of Domain Admins or Enterprise Admins. The behavior modifications of this command are as follows:
> 1. If a domain is not specified and a specific domain controller is not specified, this option returns a list of domain controllers to process from the default domain controller.
> 2. If a domain is not specified, but a domain controller is specified, a report of the certificates on the specified domain controller is generated.
> 3. If a domain is specified, but a domain controller is not specified, a list of domain controllers is generated along with reports on the certificates for each domain controller in the list.
> 4. If the domain and domain controller are specified, a list of domain controllers is generated from the targeted domain controller. A report of the certificates for each domain controller in the list is also generated.
For example, assume there is a domain named CPANDL with a domain controller named CPANDL-DC1. You could run the following command to a retrieve a list of domain controllers and their certificates that from CPANDL-DC1: certutil -dc cpandl-dc1 -dcinfo cpandl
Return to Menu
-EntInfo
CertUtil [Options] -EntInfo DomainNameMachineName$
[-f] [-user]
Return to Menu
-TCAInfo
CertUtil [Options] -TCAInfo [DomainDN | -]
Display CA information
[-f] [-enterprise] [-user] [-urlfetch] [-dc DCName] [-t Timeout]
Return to Menu
-SCInfo
CertUtil [Options] -SCInfo [ReaderName [CRYPT_DELETEKEYSET]]
Display smart card information
CRYPT_DELETEKEYSET: Delete all keys on the smart card
[-silent] [-split] [-urlfetch] [-t Timeout]
Return to Menu
-SCRoots
CertUtil [Options] -SCRoots update [+][InputRootFile] [ReaderName]
CertUtil [Options] -SCRoots save @OutputRootFile [ReaderName]
CertUtil [Options] -SCRoots view [InputRootFile | ReaderName]
CertUtil [Options] -SCRoots delete [ReaderName]
Manage smart card root certificates
[-f] [-split] [-p Password]
Return to Menu
-verifykeys
CertUtil [Options] -verifykeys [KeyContainerName CACertFile]
Verify public/private key set
KeyContainerName: key container name of the key to verify. Defaults to machine keys. Use -user for user keys.
CACertFile: signing or encryption certificate file
If no arguments are specified, each signing CA cert is verified against its private key.
This operation can only be performed against a local CA or local keys.
[-f] [-user] [-silent] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-verify
CertUtil [Options] -verify CertFile [ApplicationPolicyList | - [IssuancePolicyList]]
CertUtil [Options] -verify CertFile [CACertFile [CrossedCACertFile]]
CertUtil [Options] -verify CRLFile CACertFile [IssuedCertFile]
CertUtil [Options] -verify CRLFile CACertFile [DeltaCRLFile]
Verify certificate, CRL or chain
CertFile: Certificate to verify
ApplicationPolicyList: optional comma separated list of required Application Policy ObjectIds
IssuancePolicyList: optional comma separated list of required Issuance Policy ObjectIds
CACertFile: optional issuing CA certificate to verify against
CrossedCACertFile: optional certificate cross-certified by CertFile
CRLFile: CRL to verify
IssuedCertFile: optional issued certificate covered by CRLFile
DeltaCRLFile: optional delta CRL
If ApplicationPolicyList is specified, chain building is restricted to chains valid for the specified Application Policies.
If IssuancePolicyList is specified, chain building is restricted to chains valid for the specified Issuance Policies.
If CACertFile is specified, fields in CACertFile are verified against CertFile or CRLFile.
If CACertFile is not specified, CertFile is used to build and verify a full chain.
If CACertFile and CrossedCACertFile are both specified, fields in CACertFile and CrossedCACertFile are verified against CertFile.
If IssuedCertFile is specified, fields in IssuedCertFile are verified against CRLFile.
If DeltaCRLFile is specified, fields in DeltaCRLFile are verified against CRLFile.
[-f] [-enterprise] [-user] [-silent] [-split] [-urlfetch] [-t Timeout]
Return to Menu
-verifyCTL
CertUtil [Options] -verifyCTL CTLObject [CertDir] [CertFile]
Verify AuthRoot or Disallowed Certificates CTL
CTLObject: Identifies the CTL to verify:
- AuthRootWU: read AuthRoot CAB and matching certificates from the URL cache. Use -f to download from Windows Update instead.
- DisallowedWU: read Disallowed Certificates CAB and disallowed certificate store file from the URL cache. Use -f to download from Windows Update instead.
- AuthRoot: read registry cached AuthRoot CTL. Use with -f and a CertFile that is not already trusted to force updating the registry cached AuthRoot and Disallowed Certificate CTLs.
- Disallowed: read registry cached Disallowed Certificates CTL. -f has the same behavior as with AuthRoot.
- CTLFileName: file or http: path to CTL or CAB
CertDir: folder containing certificates matching CTL entries. An http: folder path must end with a path separator. If a folder is not specified with AuthRoot or Disallowed, multiple locations will be searched for matching certificates: local certificate stores, crypt32.dll resources and the local URL cache. Use -f to download from Windows Update when necessary. Otherwise defaults to the same folder or web site as the CTLObject.
CertFile: file containing certificate(s) to verify. Certificates will be matched against CTL entries, and match results displayed. Suppresses most of the default output.
[-f] [-user] [-split]
Return to Menu
-sign
CertUtil [Options] -sign InFileList|SerialNumber|CRL OutFileList [StartDate+dd:hh] [+SerialNumberList | -SerialNumberList | -ObjectIdList | @ExtensionFile]
CertUtil [Options] -sign InFileList|SerialNumber|CRL OutFileList [#HashAlgorithm] [+AlternateSignatureAlgorithm | -AlternateSignatureAlgorithm]
Re-sign CRL or certificate
InFileList: comma separated list of Certificate or CRL files to modify and re-sign
SerialNumber: Serial number of certificate to create. Validity period and other options must not be present.
CRL: Create an empty CRL. Validity period and other options must not be present.
OutFileList: comma separated list of modified Certificate or CRL output files. The number of files must match InFileList.
StartDate+dd:hh: new validity period: optional date plus; optional days and hours validity period; If both are specified, use a plus sign (+) separator. Use 'now[+dd:hh]' to start at the current time. Use 'never' to have no expiration date (for CRLs only).
SerialNumberList: comma separated serial number list to add or remove
ObjectIdList: comma separated extension ObjectId list to remove
@ExtensionFile: INF file containing extensions to update or remove:
HashAlgorithm: Name of the hash algorithm preceded by a # sign
AlternateSignatureAlgorithm: alternate Signature algorithm specifier
A minus sign causes serial numbers and extensions to be removed. A plus sign causes serial numbers to be added to a CRL. When removing items from a CRL, the list may contain both serial numbers and ObjectIds. A minus sign before AlternateSignatureAlgorithm causes the legacy signature format to be used. A plus sign before AlternateSignatureAlgorithm causes the alternature signature format to be used. If AlternateSignatureAlgorithm is not specified then the signature format in the certificate or CRL is used.
Adobe flash cs5.5. [-nullsign] [-f] [-silent] [-Cert CertId]
Return to Menu
-vroot
CertUtil [Options] -vroot [delete]
Create/delete web virtual roots and file shares
Return to Menu
-vocsproot
CertUtil [Options] -vocsproot [delete]
Create/delete web virtual roots for OCSP web proxy
Return to Menu
-addEnrollmentServer
CertUtil [Options] -addEnrollmentServer Kerberos | UserName | ClientCertificate [AllowRenewalsOnly] [AllowKeyBasedRenewal]
Add an Enrollment Server application
Add an Enrollment Server application and application pool if necessary, for the specified CA. This command does not install binaries or packages. One of the following authentication methods with which the client connects to a Certificate Enrollment Server.
- Kerberos: Use Kerberos SSL credentials
- UserName: Use named account for SSL credentials
- ClientCertificate: Use X.509 Certificate SSL credentials
- AllowRenewalsOnly: Only renewal requests can be submitted to this CA via this URL
- AllowKeyBasedRenewal -- Allows use of a certificate that has no associated account in the AD. This applies only with ClientCertificate and AllowRenewalsOnly mode.
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-deleteEnrollmentServer
CertUtil [Options] -deleteEnrollmentServer Kerberos | UserName | ClientCertificate
Delete an Enrollment Server application
Delete an Enrollment Server application and application pool if necessary, for the specified CA. This command does not remove binaries or packages. One of the following authentication methods with which the client connects to a Certificate Enrollment Server.
- Kerberos: Use Kerberos SSL credentials
- UserName: Use named account for SSL credentials
- ClientCertificate: Use X.509 Certificate SSL credentials
[-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-addPolicyServer
CertUtil [Options] -addPolicyServer Kerberos | UserName | ClientCertificate [KeyBasedRenewal]
Add a Policy Server application
Add a Policy Server application and application pool if necessary. This command does not install binaries or packages. One of the following authentication methods with which the client connects to a Certificate Policy Server:
- Kerberos: Use Kerberos SSL credentials
- UserName: Use named account for SSL credentials
- ClientCertificate: Use X.509 Certificate SSL credentials
- KeyBasedRenewal: Only policies that contain KeyBasedRenewal templates are returned to the client. This flag applies only for UserName and ClientCertificate authentication.
Return to Menu
-deletePolicyServer
CertUtil [Options] -deletePolicyServer Kerberos | UserName | ClientCertificate [KeyBasedRenewal]
Delete a Policy Server application
Delete a Policy Server application and application pool if necessary. This command does not remove binaries or packages. One of the following authentication methods with which the client connects to a Certificate Policy Server:
- Kerberos: Use Kerberos SSL credentials
- UserName: Use named account for SSL credentials
- ClientCertificate: Use X.509 Certificate SSL credentials
- KeyBasedRenewal: KeyBasedRenewal policy server
Return to Menu
-oid
CertUtil [Options] -oid ObjectId [DisplayName | delete [LanguageId [Type]]]
CertUtil [Options] -oid GroupId
CertUtil [Options] -oid AlgId | AlgorithmName [GroupId]
Display ObjectId or set display name
- ObjectId -- ObjectId to display or to add display name
- GroupId -- decimal GroupId number for ObjectIds to enumerate
- AlgId -- hexadecimal AlgId for ObjectId to look up
- AlgorithmName -- Algorithm Name for ObjectId to look up
- DisplayName -- Display Name to store in DS
- delete -- delete display name
- LanguageId -- Language Id (defaults to current: 1033)
- Type -- DS object type to create: 1 for Template (default), 2 for Issuance Policy, 3 for Application Policy
- Use -f to create DS object.
[-f]
Return to Menu
-error
CertUtil [Options] -error ErrorCode
Display error code message text
Return to Menu
-getreg
CertUtil [Options] -getreg [{ca|restore|policy|exit|template|enroll|chain|PolicyServers}[ProgId]][RegistryValueName]
Display registry value
ca: Use CA's registry key
restore: Use CA's restore registry key
policy: Use policy module's registry key
exit: Use first exit module's registry key
template: Use template registry key (use -user for user templates)
enroll: Use enrollment registry key (use -user for user context)
chain: Use chain configuration registry key
PolicyServers: Use Policy Servers registry key
ProgId: Use policy or exit module's ProgId (registry subkey name)
RegistryValueName: registry value name (use 'Name*' to prefix match)
Value: new numeric, string or date registry value or filename. If a numeric value starts with '+' or '-', the bits specified in the new value are set or cleared in the existing registry value.
If a string value starts with '+' or '-', and the existing value is a REG_MULTI_SZ value, the string is added to or removed from the existing registry value. To force creation of a REG_MULTI_SZ value, add a 'n' to the end of the string value.
If the value starts with '@', the rest of the value is the name of the file containing the hexadecimal text representation of a binary value. If it does not refer to a valid file, it is instead parsed as [Date][+|-][dd:hh] -- an optional date plus or minus optional days and hours. If both are specified, use a plus sign (+) or minus sign (-) separator. Use 'now+dd:hh' for a date relative to the current time.
Use 'chainChainCacheResyncFiletime @now' to effectively flush cached CRLs.
[-f] [-user] [-GroupPolicy] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-setreg
CertUtil [Options] -setreg [{ca|restore|policy|exit|template|enroll|chain|PolicyServers}[ProgId]]RegistryValueName Value
Set registry value
ca: Use CA's registry key
restore: Use CA's restore registry key
policy: Use policy module's registry key
exit: Use first exit module's registry key
template: Use template registry key (use -user for user templates)
enroll: Use enrollment registry key (use -user for user context)
chain: Use chain configuration registry key
PolicyServers: Use Policy Servers registry key
ProgId: Use policy or exit module's ProgId (registry subkey name)
RegistryValueName: registry value name (use 'Name*' to prefix match)
Value: new numeric, string or date registry value or filename. If a numeric value starts with '+' or '-', the bits specified in the new value are set or cleared in the existing registry value.
If a string value starts with '+' or '-', and the existing value is a REG_MULTI_SZ value, the string is added to or removed from the existing registry value. To force creation of a REG_MULTI_SZ value, add a 'n' to the end of the string value.
If the value starts with '@', the rest of the value is the name of the file containing the hexadecimal text representation of a binary value. If it does not refer to a valid file, it is instead parsed as [Date][+|-][dd:hh] -- an optional date plus or minus optional days and hours. If both are specified, use a plus sign (+) or minus sign (-) separator. Use 'now+dd:hh' for a date relative to the current time.
Use 'chainChainCacheResyncFiletime @now' to effectively flush cached CRLs.
[-f] [-user] [-GroupPolicy] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-delreg
CertUtil [Options] -delreg [{ca|restore|policy|exit|template|enroll|chain|PolicyServers}[ProgId]][RegistryValueName]
Delete registry value
ca: Use CA's registry key
restore: Use CA's restore registry key
policy: Use policy module's registry key
exit: Use first exit module's registry key
template: Use template registry key (use -user for user templates)
enroll: Use enrollment registry key (use -user for user context)
chain: Use chain configuration registry key
PolicyServers: Use Policy Servers registry key
ProgId: Use policy or exit module's ProgId (registry subkey name)
RegistryValueName: registry value name (use 'Name*' to prefix match)
Value: new numeric, string or date registry value or filename. If a numeric value starts with '+' or '-', the bits specified in the new value are set or cleared in the existing registry value.
If a string value starts with '+' or '-', and the existing value is a REG_MULTI_SZ value, the string is added to or removed from the existing registry value. To force creation of a REG_MULTI_SZ value, add a 'n' to the end of the string value.
If the value starts with '@', the rest of the value is the name of the file containing the hexadecimal text representation of a binary value. If it does not refer to a valid file, it is instead parsed as [Date][+|-][dd:hh] -- an optional date plus or minus optional days and hours. If both are specified, use a plus sign (+) or minus sign (-) separator. Use 'now+dd:hh' for a date relative to the current time.
Use 'chainChainCacheResyncFiletime @now' to effectively flush cached CRLs.
[-f] [-user] [-GroupPolicy] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-ImportKMS
CertUtil [Options] -ImportKMS UserKeyAndCertFile [CertId]
Import user keys and certificates into server database for key archival
UserKeyAndCertFile -- Data file containing user private keys and certificates to be archived. This can be any of the following:
- Exchange Key Management Server (KMS) export file
- PFX file
CertId: KMS export file decryption certificate match token. See -store.
Use -f to import certificates not issued by the CA.
[-f] [-silent] [-split] [-config MachineCAName] [-p Password] [-symkeyalg SymmetricKeyAlgorithm[,KeyLength]]
Return to Menu
-ImportCert
CertUtil [Options] -ImportCert Certfile [ExistingRow]
Import a certificate file into the database
Use ExistingRow to import the certificate in place of a pending request for the same key.
Use -f to import certificates not issued by the CA.
The CA may also need to be configured to support foreign certificate import: certutil -setreg caKRAFlags +KRAF_ENABLEFOREIGN
[-f] [-config MachineCAName]
Return to Menu
-GetKey
CertUtil [Options] -GetKey SearchToken [RecoveryBlobOutFile]
CertUtil [Options] -GetKey SearchToken script OutputScriptFile

CertUtil [Options] -GetKey SearchToken retrieve | recover OutputFileBaseName
Retrieve archived private key recovery blob, generate a recovery script, or recover archived keys
Paint shop pro software. Send your files to a wide selection of image formats for easy sharing.Lab RetroTake a look at your photos using the old color and contrast of the school.
script: generate a script to retrieve and recover keys (default behavior if multiple matching recovery candidates are found, or if the output file is not specified).
Certutil Hashfile Sha256
retrieve: retrieve one or more Key Recovery Blobs (default behavior if exactly one matching recovery candidate is found, and if the output file is specified)
recover: retrieve and recover private keys in one step (requires Key Recovery Agent certificates and private keys)
However, Momonga, a powerful wizard and master of the dark guild Ainz Ooal Gown, decides to spend his last few moments in the game as the servers begin to shut down. To his surprise, despite the clock having struck midnight, Momonga is still fully conscious as his character and, moreover, the non-player characters appear to have developed personalities of their own!Confronted with this abnormal situation, Momonga commands his loyal servants to help him investigate and take control of this new world, with the hopes of figuring out what has caused this development and if there may be others in the same predicament.(Source: MAL Rewrite). Download overlord anime. Alternate Title: Overlord, Overlord, オーバーロード Type: TVStatus: Finished AiringNumber of Episodes: 13 Episode(s)Date: 2015-07-07 to 2015-09-29Score: 80.43Age Rating: Violence, ProfanitySummary: The final hour of the popular virtual reality game Yggdrasil has come.
SearchToken: Used to select the keys and certificates to be recovered.
Can be any of the following:
Certutil Command Windows 10
- Certificate Common Name
- Certificate Serial Number
- Certificate SHA-1 hash (thumbprint)
- Certificate KeyId SHA-1 hash (Subject Key Identifier)
- Requester Name (domainuser)
- UPN (user@domain)
RecoveryBlobOutFile: output file containing a certificate chain and an associated private key, still encrypted to one or more Key Recovery Agent certificates.
OutputScriptFile: output file containing a batch script to retrieve and recover private keys.
OutputFileBaseName: output file base name. For retrieve, any extension is truncated and a certificate-specific string and the .rec extension are appended for each key recovery blob. Each file contains a certificate chain and an associated private key, still encrypted to one or more Key Recovery Agent certificates. For recover, any extension is truncated and the .p12 extension is appended. Contains the recovered certificate chains and associated private keys, stored as a PFX file.
[-f] [-UnicodeText] [-silent] [-config MachineCAName] [-p Password] [-ProtectTo SAMNameAndSIDList] [-csp Provider]
Return to Menu
-RecoverKey
CertUtil [Options] -RecoverKey RecoveryBlobInFile [PFXOutFile [RecipientIndex]]
Recover archived private key
Certutil Sha256
[-f] [-user] [-silent] [-split] [-p Password] [-ProtectTo SAMNameAndSIDList] [-csp Provider] [-t Timeout]
Return to Menu
-MergePFX
CertUtil [Options] -MergePFX PFXInFileList PFXOutFile [ExtendedProperties]
PFXInFileList: Comma separated PFX input file list
PFXOutFile: PFX output file
ExtendedProperties: Include extended properties
The password specified on the command line is a comma separated password list. If more than one password is specified, the last password is used for the output file. If only one password is provided or if the last password is '*', the user will be prompted for the output file password.
[-f] [-user] [-split] [-p Password] [-ProtectTo SAMNameAndSIDList] [-csp Provider]
Return to Menu
-ConvertEPF
CertUtil [Options] -ConvertEPF PFXInFileList EPFOutFile [cast | cast-] [V3CACertId][,Salt]
Convert PFX files to EPF file
PFXInFileList: Comma separated PFX input file list
EPF: EPF output file
cast: Use CAST 64 encryption
cast-: Use CAST 64 encryption (export)
V3CACertId: V3 CA Certificate match token. See -store CertId description.
Salt: EPF output file salt string
The password specified on the command line is a comma separated password list. If more than one password is specified, the last password is used for the output file. If only one password is provided or if the last password is '*', the user will be prompted for the output file password.
[-f] [-silent] [-split] [-dc DCName] [-p Password] [-csp Provider]
Return to Menu
Options
This section defines the options that you can specify with the command.
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
| -nullsign | Use hash of data as signature |
| -f | Force overwrite |
| -enterprise | Use local machine Enterprise registry certificate store |
| -user | Use HKEY_CURRENT_USER keys or certificate store |
| -GroupPolicy | Use Group Policy certificate store |
| -ut | Display user templates |
| -mt | Display machine templates |
| -Unicode | Write redirected output in Unicode |
| -UnicodeText | Write output file in Unicode |
| -gmt | Display times as GMT |
| -seconds | Display times with seconds and milliseconds |
| -silent | Use silent flag to acquire crypt context |
| -split | Split embedded ASN.1 elements, and save to files |
| -v | Verbose operation |
| -privatekey | Display password and private key data |
| -pin PIN | Smart Card PIN |
| -urlfetch | Retrieve and verify AIA Certs and CDP CRLs |
| -config MachineCAName | CA and computer name string |
| -PolicyServer URLOrId | Policy Server URL or Id. For selection U/I, use -PolicyServer. For all Policy Servers, use -PolicyServer * |
| -Anonymous | Use anonymous SSL credentials |
| -Kerberos | Use Kerberos SSL credentials |
| -ClientCertificate ClientCertId | Use X.509 Certificate SSL credentials. For selection U/I, use -clientCertificate. |
| -UserName UserName | Use named account for SSL credentials. For selection U/I, use -UserName. |
| -Cert CertId | Signing certificate |
| -dc DCName | Target a specific Domain Controller |
| -restrict RestrictionList | Comma separated Restriction List. Each restriction consists of a column name, a relational operator and a constant integer, string or date. One column name may be preceded by a plus or minus sign to indicate the sort order. Examples: 'RequestId = 47' '+RequesterName >= a, RequesterName < b' '-RequesterName > DOMAIN, Disposition = 21' |
| -out ColumnList | Comma separated Column List |
| -p Password | Password |
| -ProtectTo SAMNameAndSIDList | Comma separated SAM Name/SID List |
| -csp Provider | Provider |
| -t Timeout | URL fetch timeout in milliseconds |
| -symkeyalg SymmetricKeyAlgorithm[,KeyLength] | Name of Symmetric Key Algorithm with optional key length, example: AES,128 or 3DES |
Windows 7 Certutil Sha256
Return to Menu
Additional certutil examples
For some examples of how to use this command, see
Windows Certutil Md5
Return to Menu